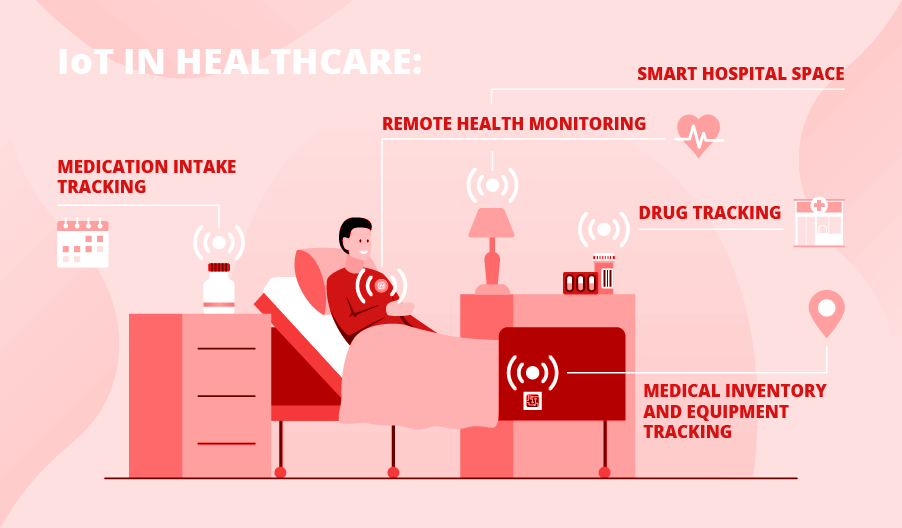
Why IoT in Healthcare Becomes a Priority
The Grand View Research report states that the IoT healthcare market will reach $534.3 billion in feature. No wonder, the majority of surveyed healthcare companies either maintained or increased their IoT budgets, according to the Gartner research. And now, the COVID-19 situation significantly contributes to the market growth, as people are urged to receive certain kinds of medical care remotely via telehealth solutions.
My experience shows that most of the visits to doctors are likely to become virtual in the future. Let’s see how IoT solutions make the healthcare environment more convenient for patients and medical staff.
What are IoT and IoMT?
My colleague Alex Grizhnevich, IoT consultant at Haus Consulting, defines Internet of Things as a network of physical devices with sensors and actuators, software, and network connectivity that enable devices to gather and transmit data and fulfill users' tasks. Today, IoT becomes a key component of the digital transformation of healthcare, so we can distinguish a separate group of initiatives, the so-called IoHT (Internet of Health Things) or IoMT (Internet of Medical Things).
Popular IoMT Use Cases
IoT-based patient care
Medication intake tracking
IoT-based medication tracking allows doctors to monitor the impact of a prescribed medication’s dosage on a patient’s condition. In their turn, patients can control medication intake, e.g., by using in-app reminders and note in the app how their symptoms change for their doctor’s further analysis. The patient app can be connected to smart devices, (e.g., a smart pill bottle) for easier management of multiple medications.
Remote health monitoring
Among examples of employing IoT in healthcare, this use case is especially viable for chronic disease management. Patients can use connected medical devices or body-worn biosensors to allow doctors or nurses to check their vitals (blood pressure, glucose level, heart rate, etc.) via doctor/nurse-facing apps. Health professionals can monitor this data 24/7 and study app-generated reports to get insights into health trends. Patients who show signs of deteriorating health are scheduled for in-person visits.
IoT- and RFID-based medical asset monitoring
Medical inventory and equipment tracking
All medical tools and durable assets (beds, medical equipment) are equipped with RFID (radio frequency identification) tags. Fixed RFID readers (e.g., on the walls) collect the info about the location of assets. Medical staff can view it using a mobile or web application with a map.
Drug tracking
RFID-enabled drug tracking helps pharmacies and hospitals verify the authenticity of medication packages and timely spot medication shortages.
Smart hospital space
Cloud-connected ward sensors (e.g., a light switch, door and window contacts) and ambient sensors (e.g., hydrometers, noise detectors) allow patients to control their environment for a comfortable hospital stay.
Advantages of using IoT technology in healthcare
Patient-centric care
Medical IoT helps turn patients into active participants of the treatment process, thus improving care outcomes. Besides, IoMT helps increase patient satisfaction with care delivery, from communication with medical staff to physical comfort (smart lighting, climate control, etc.).
Reduced care-related costs
Non-critical patients can stay at home and use cloud-connected medical IoT devices, which gather, track and send health data to the medical facility. And with the help of telehealth technology, patients can schedule e-visits with nurses and doctors without traveling to the hospital.
Reduced readmissions
Patient apps connected to biosensors help ensure compliance with a discharge plan, enable prompt detection of health state deviations, and provide an opportunity to timely contact a health professional remotely.
Challenges of IoMT and how to address them
Potential health data security breaches
The connected nature of IoT brings about information security challenges for healthcare providers and patients.
We recommend implementing HIPAA-compliant IoMT solutions and conduct vulnerability assessment and penetration testing regularly to ensure the highest level of protection.
Integration difficulties
Every medical facility has its unique set of applications to be integrated with an IoMT solution (e.g., EHR, EMR). Some of these applications may be heavily customized or outdated.
Develop the integrations strategy from the start of your IoMT project, including the scope and the nature of custom integrations.
Enhance care delivery with IoMT
According to my estimates, the use of IoT technology in healthcare will continue to rise during the next decade, driven by the impact of the COVID situation and the growing demand for remote care. If you need help with creating and implementing a fitting IoMT solution, you’re welcome to turn to Haus Consulting healthcare IT team.